what is crontab
The Cron daemon is a built-in Linux utility that runs processes on your system at a scheduled time. Cron reads the crontab (cron tables) for predefined commands and scripts.
By using a specific syntax, you can configure a cron job to schedule scripts or other commands to run automatically.
This guide shows you how to set up a cron job in Linux, with examples.
Prerequisites
- A system running Linux
- Access to a command line/terminal window (Ctrl–Alt–T or Ctrl–Alt–F2)
- A user account with root or sudo privileges
Basic Crontab Syntax
To be able to set up a cron job, we need to understand the basic elements that make up this syntax. The standard form for a crontab line is as follows:
a b c d e /directory/command output
So, the parts of a cron command are:
1. The first five fields a b c d e specify the time/date and recurrence of the job.
2. In the second section, the /directory/command specifies the location and script you want to run.
3. The final segment output is optional. It defines how the system notifies the user of the job completion.
1.Cron Job Time Format
The first five fields in the command represent numbers that define when and how often the command runs. A space separates each position, which represents a specific value.
The table below summarizes possible values for the fields and the example syntax:
2.Command to Execute
The next section specifies the command to execute. It represents the exact directory and filename of the script or commands you want cron to complete. For example:
/root/backup.shIn our example, the command looks at the root directory of the system and runs the backup.sh script. You may specify any script or command you wish.
3.Output (Optional)
By default, cron sends an email to the owner of the crontab file when it runs. This is a convenient way to keep track of tasks. Keep in mind that regular or minor tasks can fill up your inbox quickly.
As this is an optional feature, you can prevent that scenario by disabling the output email. To turn off email output, add the following string, >/dev/null 2>&1, after the timing and command fields.
* * * * * directory/command >/dev/null 2>&14.Using Operators (Optional)
For efficiency, cron syntax also uses operators. Operators are special characters that perform operations on the provided values in the cron field.
- An asterisk (*) stands for all values. Use this operator to keep tasks running during all months, or all days of the week.
- A comma (,) specifies separate individual values.
- A dash (–) indicates a range of values.
- A forward-slash (/) is used to divide a value into steps. (*/2 would be every other value, */3 would be every third, */10 would be every tenth, etc.)
Setting Up a Cron Job
To configure a cron job, open the crontab with a preferred text editor and input the syntax for the command you want to run.
How to Edit the crontab File?
To open the crontab configuration file for the current user, enter the following command in your terminal window:
crontab –eYou can add any number of scheduled tasks, one per line.
Once you have finished adding tasks, save the file and exit. The cron daemon will read and execute the instructions provided.
Remember, Cron does not need to be restarted to apply changes.
Edit crontab for a Different User
To edit the crontab for a another user, enter the following command:
crontab –u other_username –eNote: If you need to run a cron job on reboot, please refer to our Crontab on Boot guide.
Cron job examples
* 2 0 * 4 /root/backup.shEven though it’s set to run at 2 am, it only runs when the first of the month (0) falls on a Wednesday (4). If you change to the following:
* 2 0 * * /root/backup.shThe command runs the first of every month at 2 am. The following table provides a few basic commands using the /root/backup.sh file from our previous examples.
Using Special Characters
*/15 * * * *The * means all values, and the /15 counts and repeats every 15th minute.
2-Use the dash character to specify a range. To run the code every weekday at 4 am:
0 4 * * 1-5 /root/backup.shIn this case, 1-5 specifies Monday – Friday.
3-Use a comma to specify individual instances when the code should run:
0 4 * * 2,4 /root/backup.shThis would run the code at 4 am on Tuesday and Thursday.
4-Some wildcards can be combined. Make the command run every other day at 37 minutes past the hour:
37 1-23/2 * * * /root/backup.sh1-23 specifies the range of hours, /2 sets the interval to every other hour.
List Existing Cron Jobs
You can list all cron jobs on your system without opening the crontab configuration file. Type in the following command in a terminal window:
crontab –l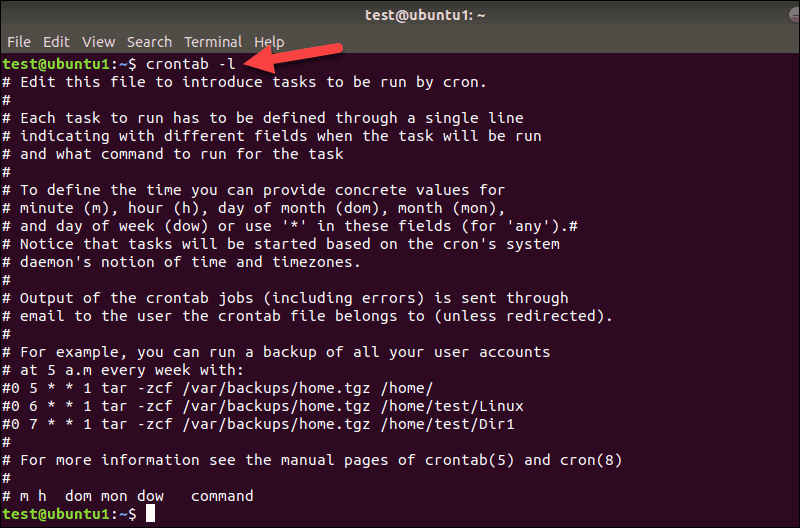
Conclusion
You now have a good understanding of how to use cron to schedule tasks in Linux. Use the examples presented in this tutorial to create and schedule cron jobs on your system. Over time, expand the tasks by using special characters to automate most of your mundane tasks.












Post a Comment
0 Comments
🔴Subscribe TechSet for the latest updates 👇https://bit.ly/2Jkdzb0
Watch the tutorials on YouTube For better understanding and if you have any doubt please let me know.